|
|
Objectives
Testing Vision
General Instructions
- Observe how the person uses vision, coming into the room or where you are testing
- Examine the eyes- what unhealthy signs do you see?
- Take a history related to eyes and vision.
Ask the person or family questions such as:
When was poor vision first noticed?
Does anyone else in your family have poor vision? What is the cause?
Have you had any treatment for poor vision?
Do you have glasses or contact lenses? When should they be used?
What can you tell me about your vision?
- Decide which test to use.
Establish how to communicate with the person being tested
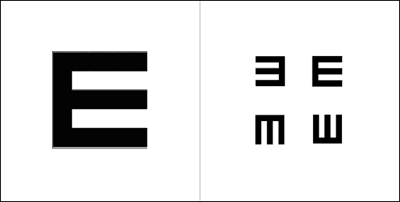
- matching symbols
- pointing directions
- naming symbols
This will depend on age. Children from 5 years of age can do the E test. Symbols or numbers can be used for younger children. Children who cannot name symbols or numbers can use a 'matching card'.
Language. The E test is useful for people who cannot read and if you do not speak the same language as the person being tested. It is also useful to use with people who are hearing impaired or deaf. You can explain how to do the test using imitation.
Teach how to do the test
Test distance acuity
a. both eyes
b. Right and left eye separately, if needed
c. If needed, use pinhole
both eyes or R & L separately if neededd. Record findings
Note: Read the test instructions of each test carefully
Test near visual acuity
both eyes together
Tell the person to hold the card where the E's are clearest
Record the smallest size read and the distance that the card is held from the eyes
|
|