|
|
The Visual System
The eye
The eye and brain work together to form images, the things we see. For good vision the pathway of light through the cornea, lens and fluids in the eye has to be clear. The light rays are focused at the back of the eye. The fluids in the eye (aqueous and vitreous) maintain the correct shape and pressure in the eye.
Media (Cornea, Lens & Vitreous)
The cornea, lens and vitreous should all be clear to transmit light to the retina. If any of them are cloudy, vision problems include glare, reduced contrast sensitivity, and possibly reduced visual acuity.
Retina
There are 2 types of receptors in the retina:
Rods
- function best in low illumination (e.g. at night or in dull areas)
- cannot discriminate colour
- are distributed mostly in the outer retina
- detect objects and movement of objects in the peripheral visual field
Cones
- enable us to see colour
- function best in good illumination
- detect and identify fine detail in objects
- are distributed mostly in the central retina, particularly the macula
Macula
- most important area to see fine detail for near and distance vision
- the area of retina which receives information from the object that the eye is directly looking at
- has a high concentration of cone cells
- degeneration of the macula common in older people (Age-Related Macular Degeneration- AMD) is rare in children
If the retina is damaged by disease, visual acuity and visual fields may be affected. The functions affected depend on the part of the retina affected.
Optic Nerve
- pathway that transmits or sends messages from the eye, to the area of the brain that gives meaning to the things that we see
Shape of the eye
- integrity of the globe and its components
- refractive errors (see "common causes of low vision")
It is important to understand that there is a difference in reduced vision due to refractive error which can be corrected with glasses and reduced vision which cannot be treated. The conditions which can be treated with medication or surgery include cataract, glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
Refractive Errors
Refractive Errors occur when the eye is not the right shape or size so that light cannot focus on the retina. Vision is blurry and can usually be corrected with glasses.
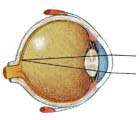
Normal Vision
Light rays pass through the cornea and lens then focus on the retina in a precise way without blurring - just as a camera lens focuses light onto a film.
The perfect state of focusing exactly on the retina is unusual; the average person is a little hyperopic (longsighted, also called hypermetropia).Myopia
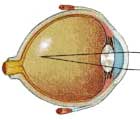
Short sightedness. This means that details can be seen up close without glasses but objects at a distance looked blurred.
The eyeball is too long and the light is focused in front of the retina making a blurred image. A concave lens, such as glasses or contact lens, makes the light focus over a longer distance so that the image falls on the retina and is seen clearly.Hypermetropia
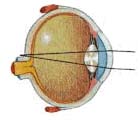
Long-sightedness. A person will have more difficulty seeing things up close without glasses
The eyeball is too short and the light is focused behind the retina making a blurred image. A convex lens, such as glasses or contact lens, makes the light focus over a shorter distance so that the image falls on the retina and is seen clearly.Astigmatism
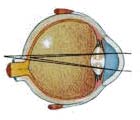
Astigmatism occurs when the front of the eye is not rounded like a ball but is squashed so that it is curved more in one direction. This makes the image on the retina blurred in one direction. A cylindrical lens makes the light focus in that direction so that all of the image becomes clear again. Astigmatism can also occur with long or shortsightedness.
|
|
| Visual Communication Unit |